This repository contains a slide-based presentation on Merkle Trees, built with Manim and manim-slides. It explains the fundamentals of Merkle Trees, their role in ensuring data integrity, and examples of their usage in modern technologies like Bitcoin and BitTorrent.
| Slide # | Title | Time (minutes) | Content | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Title Slide | - | Title: "Understanding Merkle Trees: Ensuring Data Integrity and History" | - Welcome everyone, introduce the presentation topic, and state the goal. |
| 2 | Agenda | - | Outline: Overview of key sections: Problem, Hash Functions, Merkle Trees, Usage, Q&A, Quiz | - Roadmap for the presentation, mention the quiz to keep audience engaged. |
| 3 | The Problem | 1 | Challenge: Ensuring data integrity in distributed systems. | - Encourage audience participation with a question. |
| 4 | Introduction to Hash Functions | 2 | Definition and Properties of Hash Functions: Deterministic, Pre-image resistance, Collision resistance, Fast computation | - Use analogies for ease of understanding. |
| 5 | Visualizing Hash Functions | 1 | Animation: Data input transformed into a unique hash output. | - Simple animation to reinforce understanding of hash functions. |
| 6 | Building Blocks of Merkle Trees | 2 | Concept: Combining hashes of individual data blocks to form a tree. | - Explain hierarchical structure and its benefits. |
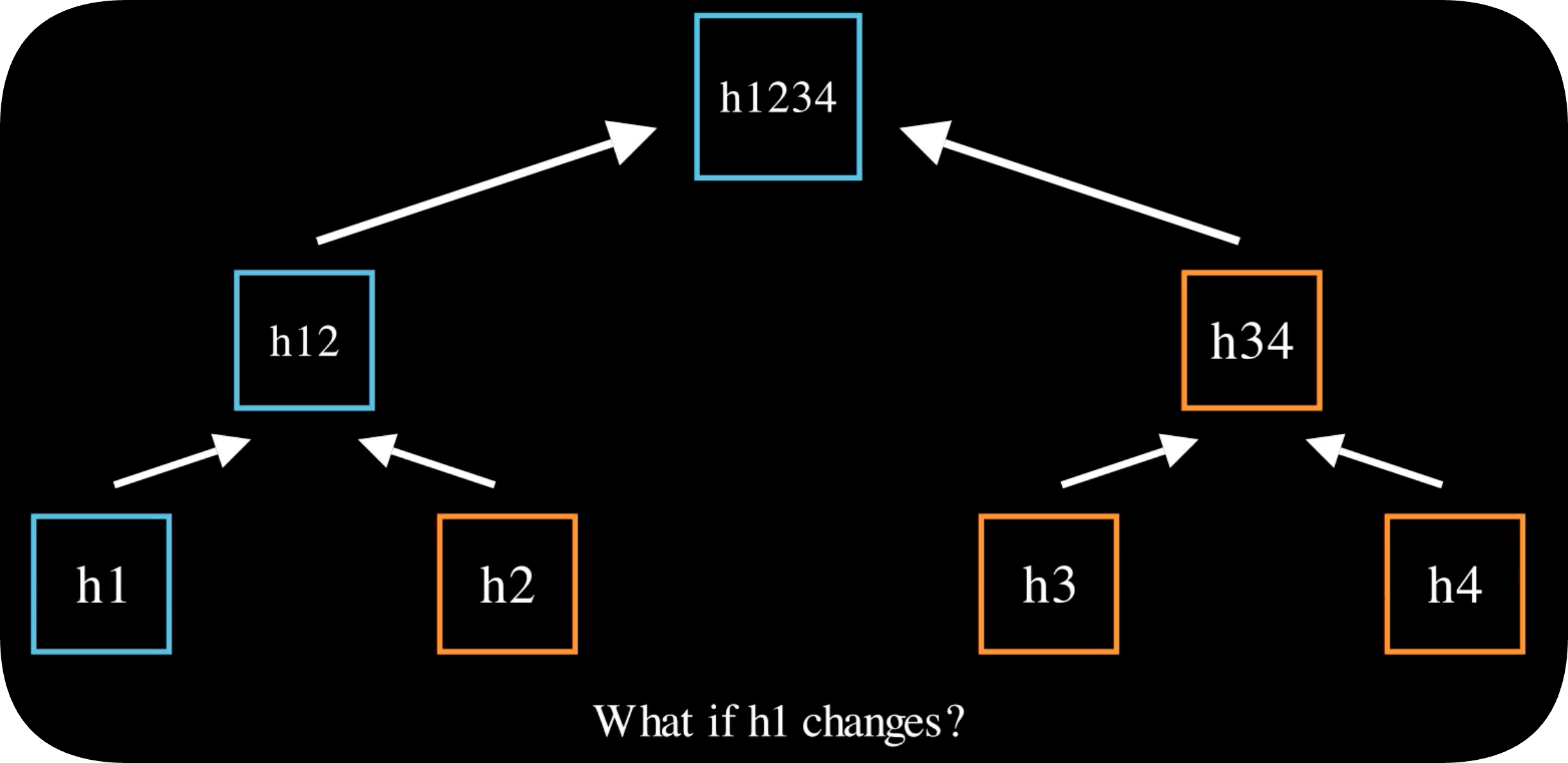
| 7 | What is a Merkle Tree? | 2 | Definition: A tree where each non-leaf node is a hash of its children. | - Highlight the root hash as the summary of all data. |
| 8 | How Merkle Trees Work | 2 | Step-by-Step Animation: Hashing individual blocks, forming parents, reaching the root hash. | - Emphasize efficiency in verifying data integrity. |
| 9 | Example Usage - BitTorrent | 3 | Explanation: Piecewise file verification with Merkle Trees. | - Mention reduced bandwidth usage in file sharing. |
| 10 | (skipped) Example Usage - Git | - | Explanation: How Merkle Trees ensure codebase integrity and track changes. | - Explain how Git uses hashes to link commits. |
| 11 | Example Usage - Bitcoin | 3 | Explanation: Transaction verification in Bitcoin blocks. | - Simplify blockchain complexity while highlighting Merkle Trees' role in integrity. |
| 12 | (skipped) Example Usage - Database Management Systems | - | Explanation: Data synchronization and integrity checks in distributed databases. | - Real-world example of Merkle Trees in DBMS. |
| 13 | Benefits of Merkle Trees | 2 | Summary: Efficient verification, tamper-evidence, scalability. | - Reinforce why Merkle Trees are important in modern technology. |
| 14 | Quiz Introduction | - | Announcement: Interactive quiz to test understanding. | - Briefly explain the format of the quiz to maintain audience engagement. |
You can run the presentation using one of the following methods:
This repository includes a convenient script called present.sh that renders and converts the presentation to HTML in one step.
-
Ensure the script has executable permissions:
chmod +x present.sh -
Run the script:
./present.sh
The script will render the presentation and open it in your default browser.
If you prefer to manually run the commands, follow these steps:
-
Render the Presentation:
manim-slides render presentation.py MerkleTreePresentation -
Convert and Open the Presentation:
manim-slides convert MerkleTreePresentation presentation.html --open
This will generate an HTML file and open it in your browser.
To build and run the project from scratch:
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/your-username/merkle-tree-presentation.git cd merkle-tree-presentation -
Set up a Python virtual environment (recommended):
python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate -
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt -
Check if you need to install external dependencies for manim-ce
-
Check if you need to install external dependencies for manim-slides
Now, you can run the presentation as described in the Running the Presentation section.